We’ve all been told that green tea is good for us, but there are still some non-believers out there.
I’ve looked into the main green tea ingredients to get a better idea of what’s in our cup of tea.
First off, let’s get the lingo right. With so many words used to talk about green tea, it can all get confusing.
It all starts with polyphenols. Green tea contains 20-45% polyphenols by weight.
Polyphenols have amazing health benefits (antioxidant, anti-aging, anti-carcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, and cardiovascular protection) and occur naturally in fruits, vegetables, wine, tea, extra virgin olive oil, chocolate, and cocoa.
There are thousands of different kinds of polyphenols, so they are divided into subcategories: diferuloylmethane, flavonoids, stilbenes, phenolic acids, and tannins.
Most of the polyphenols in our diet are in the form of flavonoids, so the two words are often used synonymously.
The most abundant flavonoids in our diet are flavanols. Flavanols are found in apples, apricots, grapes, peaches, nectarines, pears, plums, raisins, raspberries, cherries, blackberries, blueberries, cranberries, wine, chocolate, cocoa, and tea.
In the category of flavanols are catechins. In green tea, 60-80% of the polyphenols are catechins. And, of the catechins, EGCG is the most potent.
Catechins in green tea:
The amount of green tea polyphenols depends on many factors: processing of leaves (fermented vs. unfermented), geographical location, growing conditions (soil, climate, fertilizers), preparation of tea (amount of tea, temperature of water, brewing time), and the age of the leaves at harvest.
For example, the process of fermenting, such as in black and oolong teas, results in less EGCG. Also, younger leaves used for teas such as matcha and sencha contain less EGCG than mature leaves used for teas such as bancha.
Green tea also contains vitamins, minerals, and tannins.
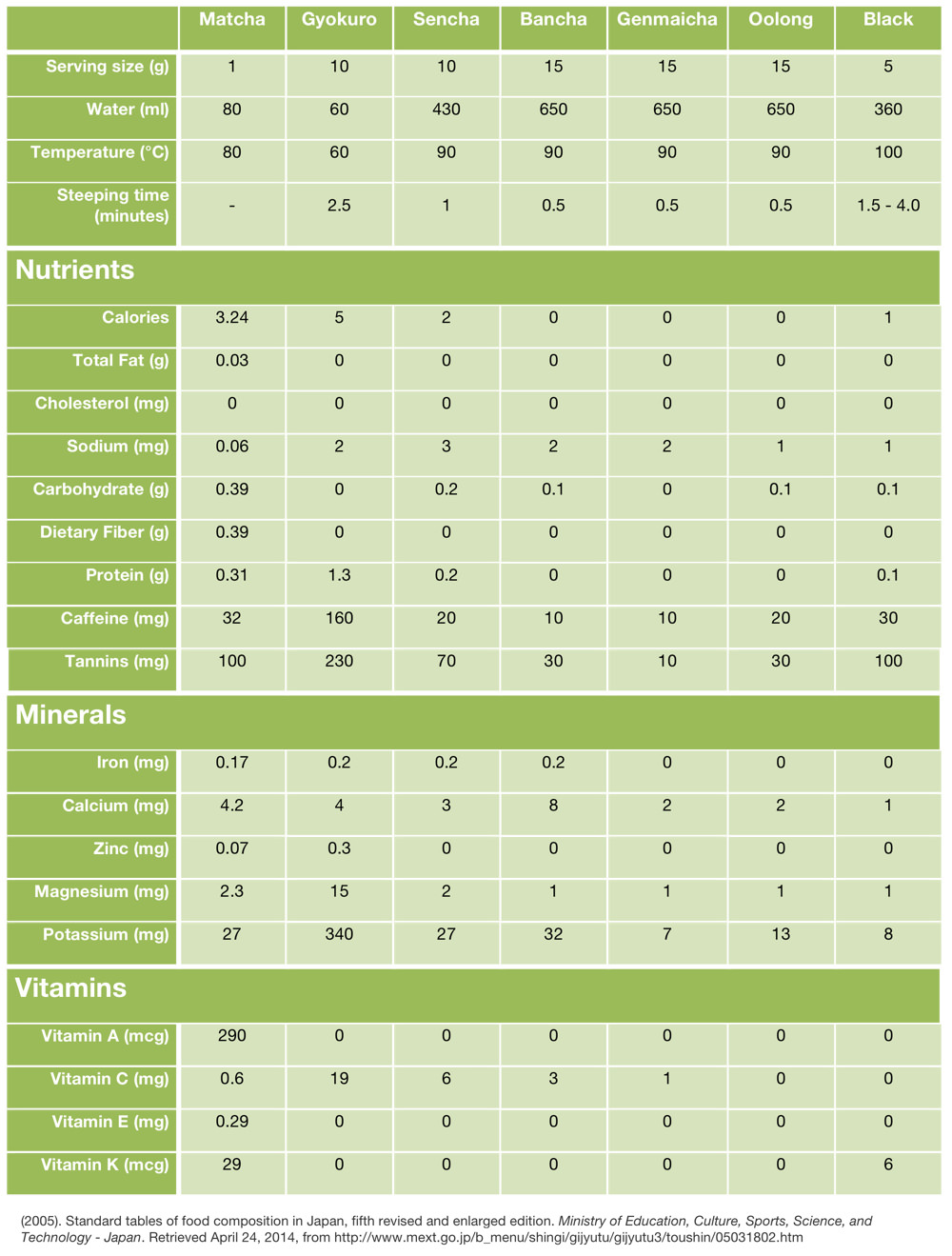 List of ingredients in Green Tea
List of ingredients in Green Tea
Dietary fiber: Effective in the prevention of colon cancer.
Caffeine: Has a diuretic effect and is responsible for the bitterness in green tea.
Tannin: A type of polyphenol responsible for the astringency or dry, puckering feeling in your mouth.
Minerals: Rich in potassium and also includes calcium, magnesium, iron, and zinc.
Fluorine: Prevents tooth decay.
L-Theanine: An amino acid that calms the effect of the caffeine and creates the sweet after-taste in green tea.
Vitamin A: Beta-carotene is an antioxidant responsible for maintenance of the respiratory and digestive systems.
Vitamin C: Eases fatigue and prevents colds. Green tea contains as much as a cup of spinach.
Vitamin E: Effective in anti-aging.
Cabrera, C., Artacho, R., & Giménez, R. (2006). Beneficial effects of green tea – A review. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 25(2), 79-99.
Han, X., Shen, T. & Lou, H. (2007). Dietary polyphenols and their biological significance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 8, 950-988.
Kiefer, D. (2011). A review of the clinical effects of green tea: Up-to-date reasons to imbibe. Alternative Medicine Alert, 14(12), 133-144.


